Woven Fabric Style Guide
Technical textiles have revolutionized various industries with their unique properties and applications. At the forefront of this revolution are high-performance materials like carbon fiber and Aramid, known for their exceptional strength and durability.
The world of technical woven fabrics is complex, with a myriad of options available, including Glass fiber and Kevlar. Understanding these materials is crucial for designers and industries looking to leverage their benefits.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide an accessible introduction to these advanced materials, exploring their composition, properties, and applications.
Key Takeaways
- Overview of technical woven fabrics
- Properties and applications of carbon fiber and Aramid
- Role of Glass fiber and Kevlar in technical textiles
- Industry applications of high-performance materials
- Design considerations for technical woven fabrics
The World of Technical Woven Fabrics
Technical woven fabrics have revolutionized various industries with their exceptional strength and durability. These engineered materials are designed to meet specific performance criteria, making them crucial in many fields.
What Makes a Fabric “Woven”
A fabric is considered “woven” when it is created by interlacing two or more sets of yarns at right angles to each other. This interlacing pattern provides strength and stability to the fabric. The primary components of a woven fabric include:
- Warp yarns: These are the yarns that run lengthwise in the fabric.
- Weft yarns: These yarns intersect the warp yarns, running widthwise.
The interaction between warp and weft yarns determines the fabric’s overall performance and characteristics.
The Importance of Weave Patterns in Performance
Weave patterns significantly influence the properties of technical woven fabrics. Different patterns can enhance various attributes such as strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors. Common weave patterns include:
- Plain weave
- Twill weave
- Satin weave
Each pattern has its advantages and is chosen based on the intended application of the fabric. For instance, a plain weave offers simplicity and durability, while a satin weave provides a smooth surface and flexibility.
The Evolution of High-Performance Textiles
From humble beginnings to the sophisticated materials of today, the evolution of high-performance textiles is a story of continuous innovation. Understanding this journey is crucial for appreciating the capabilities and limitations of modern technical textiles.
Historical Development
The development of high-performance textiles has its roots in historical advancements. Early innovations were driven by the need for stronger, more durable materials in various industries. For instance, the introduction of synthetic fibers in the early 20th century marked a significant turning point, enabling the creation of materials with enhanced strength and resistance properties.
Modern Manufacturing Innovations
Today, high-performance textiles are at the forefront of material science, with modern manufacturing techniques playing a crucial role. Advances in weaving technology, finishing treatments, and the development of new fiber types have expanded the potential applications of these materials. Techniques such as 3D weaving and the integration of smart textiles are pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
| Innovation | Impact | Industry Application |
|---|---|---|
| Synthetic Fibers | Enhanced strength and durability | Aerospace, Automotive |
| 3D Weaving | Complex structures with improved integrity | Medical, Sports Equipment |
| Smart Textiles | Integration of technology for real-time monitoring | Healthcare, Wearables |
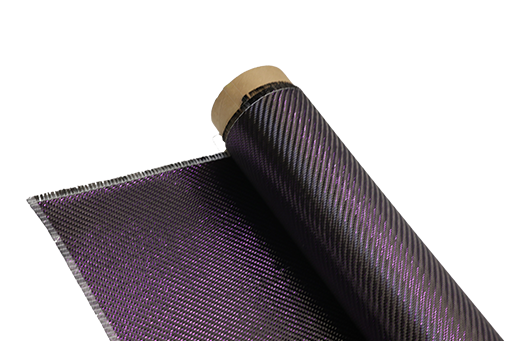
Carbon Fiber Woven Fabric: The Ultimate Strength-to-Weight Material
With its unique blend of strength and lightness, carbon fiber woven fabric is transforming the world of materials science. This exceptional material is renowned for its outstanding strength-to-weight ratio, making it a highly sought-after choice for various industrial applications and design applications.
Composition and Microstructure
Carbon fiber woven fabric is composed of carbon fibers that are woven together to form a fabric. The microstructure of this material is characterized by its high degree of crystallinity and the alignment of carbon fibers, which contribute to its exceptional mechanical properties.
The microstructure plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance of the fabric, including its tensile strength, stiffness, and resistance to deformation.
Visual and Tactile Characteristics
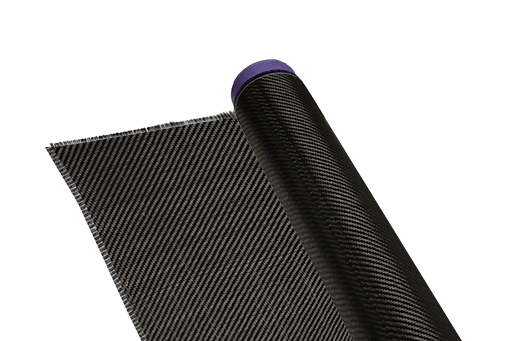
The visual appearance of carbon fiber woven fabric is distinct, often featuring a woven pattern that can vary depending on the specific weave type. The fabric typically has a dark color, often black, due to the carbon content.
Tactilely, the fabric can feel stiff and rigid, reflecting its high stiffness and strength. The surface texture can vary based on the weave pattern and any additional treatments or coatings applied to the fabric.
Common Applications in Industry and Design
Carbon fiber woven fabric is utilized in a wide range of industrial applications, including aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment manufacturing, where its strength-to-weight ratio is particularly valuable.
- Aerospace: Lightweight components for aircraft and spacecraft.
- Automotive: High-performance vehicle parts, such as body panels and engine components.
- Sports Equipment: Bicycle frames, golf clubs, and other equipment where reduced weight and increased strength are beneficial.
In design applications, carbon fiber woven fabric is prized for its unique aesthetic and functional properties, often used in luxury goods, high-end sports cars, and innovative architectural elements.
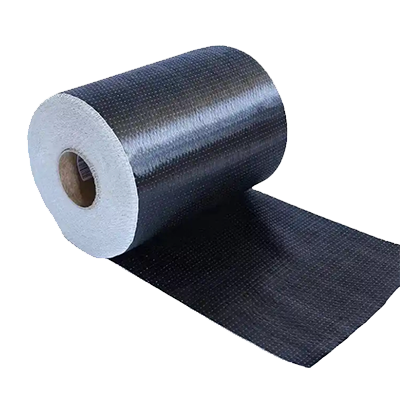
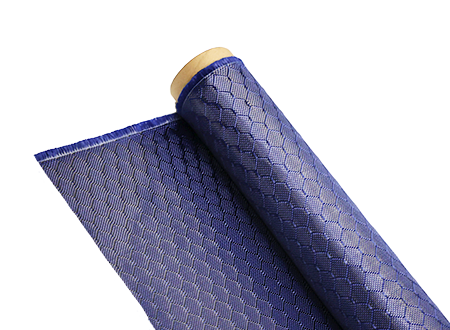
Glass Fiber Woven Materials: Balancing Cost and Performance
Glass fiber woven materials offer a compelling combination of cost-effectiveness and high performance, making them suitable for a wide range of uses. Their versatility is a key factor in their widespread adoption across various industries.
E-Glass, S-Glass, and Specialty Variants
Glass fiber woven materials come in several types, each with its unique characteristics. E-Glass is the most commonly used variant, known for its excellent electrical insulation properties and cost-effectiveness. S-Glass, on the other hand, offers higher strength and stiffness, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Specialty variants, such as C-Glass and E-CR Glass, provide enhanced chemical resistance and other tailored properties.
Thermal and Electrical Properties
Glass fiber woven materials exhibit excellent thermal stability, making them suitable for applications where temperature resistance is crucial. Their electrical insulation properties are also noteworthy, particularly for E-Glass, which is widely used in electronics. The table below summarizes the key thermal and electrical properties of different glass fiber types.
| Glass Fiber Type | Thermal Stability (°C) | Electrical Resistivity (Ω·cm) |
|---|---|---|
| E-Glass | Up to 600 | 10^14 |
| S-Glass | Up to 800 | 10^15 |
| C-Glass | Up to 700 | 10^13 |
Practical Applications in Various Industries
Glass fiber woven materials are used in a variety of industries, including construction, automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Their applications range from reinforced composites and insulation materials to printed circuit boards and filtration systems. The choice of glass fiber type depends on the specific requirements of the application, including factors such as strength, thermal resistance, and electrical properties.
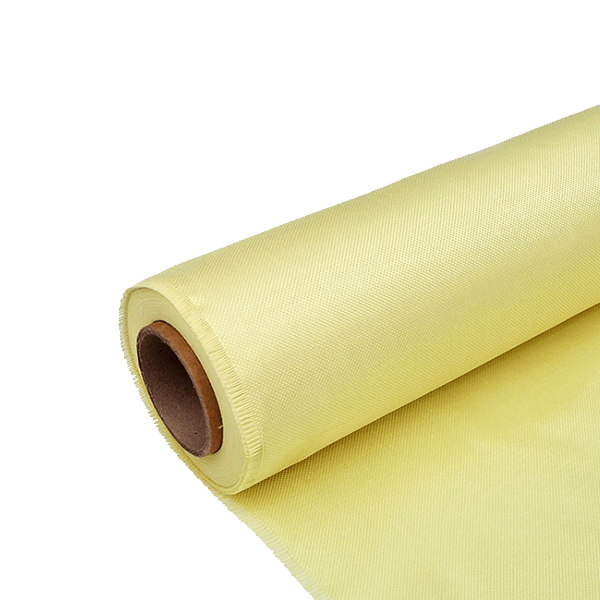
Aramid Woven Fabrics: When Heat and Abrasion Resistance Matter
Aramid woven fabrics are engineered to provide superior protection against heat, flames, and abrasion. This makes them a critical component in various safety and protective applications.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Aramid fibers are characterized by their unique chemical composition, which involves a rigid molecular structure that provides exceptional strength and resistance to heat. The aromatic polyamide chains in aramid fibers are highly oriented, contributing to their remarkable durability.
Heat and Flame Resistance Properties
One of the standout features of aramid woven fabrics is their outstanding heat and flame resistance. Unlike many other materials, aramid fabrics do not melt or ignite easily, making them ideal for applications where exposure to high temperatures is a concern.
Applications in Safety and Protection
The safety applications of aramid woven fabrics are diverse, ranging from protective gear for firefighters to industrial protective clothing. Their ability to withstand abrasion and heat makes them a preferred choice for manufacturing gloves, helmets, and other safety equipment.
In conclusion, aramid woven fabrics offer a unique combination of heat resistance, abrasion resistance, and durability, making them indispensable in various safety-critical applications.
Kevlar Woven Textiles: Beyond Bulletproof Applications
While Kevlar is often associated with ballistic protection, its versatility and strength make it suitable for a wide range of innovative applications. Kevlar woven textiles are renowned for their exceptional mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and resistance to heat and flames.
Distinguishing Kevlar from Other Aramids
Kevlar is a type of aramid fiber, but not all aramids are Kevlar. The key distinction lies in its para-aramid structure, which provides superior strength and resistance to heat compared to meta-aramid fibers. This unique molecular structure is responsible for Kevlar’s outstanding performance in various applications.
Impact and Puncture Resistance
One of Kevlar’s most significant advantages is its outstanding impact and puncture resistance. This property makes it an ideal material for protective gear, including gloves, helmets, and body armor. The fabric’s ability to absorb and dissipate energy upon impact is crucial in these applications.
- High energy absorption capacity
- Excellent puncture resistance
- Flexibility and comfort in wear
Kevlar’s impact resistance is not limited to protective gear; it’s also valuable in industrial applications where materials are subject to wear and tear.
Innovative Uses in Consumer Products
Beyond its traditional uses, Kevlar is being incorporated into various consumer products, enhancing their durability and performance. Some examples include:
- Sports equipment, such as bicycle tires and hockey sticks
- High-performance composites for automotive and aerospace applications
- Protective cases for electronic devices

The use of Kevlar in these products not only improves their strength and durability but also contributes to their lightweight and flexible design. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of Kevlar woven textiles in the consumer market.
Essential Weave Patterns for Technical Woven Fabrics
Technical woven fabrics owe their performance characteristics to their weave patterns, which are crucial in determining their suitability for various applications. The weave pattern significantly influences the fabric’s strength, durability, and overall functionality.
Plain Weave Characteristics
The plain weave is one of the most basic and widely used weave patterns. It is characterized by a simple over-and-under pattern of yarns. This weave provides a good balance between stability and flexibility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Twill Weave Variations
Twill weave fabrics are known for their diagonal rib pattern, which is achieved by passing the weft yarn over multiple warp yarns. This weave offers improved flexibility and drape compared to plain weave, along with enhanced durability.
Satin and Harness Satin Options
Satin weave and harness satin are known for their smooth surface and high luster. These weaves are achieved by floating the yarns over multiple intersections, resulting in a fabric with high flexibility and a luxurious appearance.
Performance Differences Between Weave Types
The performance of technical woven fabrics varies significantly with different weave patterns. For instance, plain weave offers high stability, while twill weave provides better flexibility. Satin and harness satin weaves are known for their aesthetic appeal and are often used in applications where appearance is crucial.
Comparing Carbon Fiber, Glass Fiber, Aramid, and Kevlar Woven Fabrics
When it comes to selecting the ideal technical woven fabric, understanding the differences between carbon fiber, glass fiber, aramid, and Kevlar is crucial. Each of these materials offers unique properties that make them suitable for various applications across different industries.
Strength and Weight Considerations
Carbon fiber woven fabrics are renowned for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for applications where minimizing weight is critical, such as in aerospace and high-performance sports equipment. In contrast, glass fiber fabrics, while strong, are generally heavier and less expensive than carbon fiber. Aramid and Kevlar fabrics offer excellent tensile strength and are often used in ballistic protection and high-temperature applications.
Durability and Lifespan Factors
The durability of these fabrics varies significantly. Carbon fiber is highly resistant to fatigue but can be brittle and prone to damage from impact. Glass fiber fabrics are durable but can degrade over time when exposed to certain environmental conditions. Aramid and Kevlar fabrics are known for their resistance to abrasion and heat, contributing to their long lifespan in demanding applications.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Cost is a critical factor in material selection. Carbon fiber fabrics are typically the most expensive due to the complex manufacturing process involved. Glass fiber fabrics are generally more affordable, making them a popular choice for large-scale industrial applications. Aramid and Kevlar fabrics fall somewhere in between in terms of cost, reflecting their high-performance capabilities.
Hybrid Fabric Solutions
In some cases, combining different materials can offer the best of multiple worlds. Hybrid fabric solutions blend the benefits of various fibers, such as the strength of carbon fiber and the cost-effectiveness of glass fiber, to create materials tailored to specific application requirements. This approach allows for optimized performance and cost efficiency.
By carefully comparing the properties of carbon fiber, glass fiber, aramid, and Kevlar woven fabrics, manufacturers and designers can make informed decisions that balance performance, durability, and cost. Whether for industrial, aerospace, or protective gear applications, understanding these differences is key to selecting the most appropriate material.
Finishing and Treatment Options for Technical Textiles
Finishing and treatment options play a crucial role in determining the suitability of technical textiles for specific applications. These processes can significantly enhance the performance, durability, and functionality of technical textiles, making them more versatile and effective in various industries.
Resin Compatibility Considerations
When it comes to technical textiles, resin compatibility is a critical factor. The choice of resin can affect the textile’s mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and overall performance. For instance, carbon fiber textiles are often used with epoxy resins to create high-strength composites. Ensuring compatibility between the textile and resin is vital for achieving optimal results.
Surface Treatments and Coatings
Surface treatments and coatings can improve the properties of technical textiles, such as water resistance, UV stability, and abrasion resistance. Techniques like plasma treatment, sol-gel coating, and nanocoating can be applied to enhance the textile’s performance. According to a study, “Surface modification of textiles can significantly improve their functionality and extend their service life”
Advanced Textile Materials and Processes, 2020

| Finishing Technique | Benefits | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Plasma Treatment | Improved surface adhesion, enhanced wettability | Composites, medical textiles |
| Sol-Gel Coating | Enhanced durability, improved chemical resistance | Aerospace, industrial textiles |
| Nanocoating | Improved water resistance, UV protection | Outdoor gear, protective clothing |
Edge Finishing Techniques
Edge finishing techniques are essential for preventing fraying and improving the overall quality of technical textiles. Methods such as laser cutting, ultrasonic welding, and serging can be used to finish edges. The choice of technique depends on the type of textile and its intended application.
Sourcing Quality Technical Woven Fabrics
The process of sourcing technical textiles requires a comprehensive understanding of material specifications and manufacturing processes. Ensuring the quality of these materials is crucial for the success of various industrial applications.
Evaluating Manufacturer Specifications
When sourcing technical woven fabrics, it’s essential to evaluate the manufacturer’s specifications carefully. This includes understanding the material composition, weave pattern, and any special treatments or finishes applied to the fabric.
Testing and Certification Standards
Technical textiles must meet specific testing and certification standards to ensure their performance and safety. Look for fabrics that comply with relevant industry standards, such as those set by ASTM or ISO.
Small Quantity vs. Production Volume Purchasing
Deciding between small quantity and production volume purchasing depends on your project’s needs. Small quantities are ideal for prototyping or small-scale applications, while production volumes are better suited for large-scale industrial use.
| Purchasing Considerations | Small Quantity | Production Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Cost per Unit | Higher | Lower |
| Lead Time | Shorter | Longer |
| Application Suitability | Prototyping, small projects | Large-scale industrial applications |
By carefully evaluating manufacturer specifications, adhering to testing and certification standards, and considering your purchasing needs, you can source high-quality technical woven fabrics that meet your project’s requirements.
Care, Maintenance and Handling Best Practices
To ensure the longevity of technical woven fabrics, it’s essential to follow best practices in care and maintenance. Proper handling and storage can significantly impact the performance and lifespan of these materials.
Storage Requirements
Technical woven fabrics should be stored in a cool, dry environment, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Proper storage involves keeping the fabrics flat or rolled, depending on their type and size, to prevent creases and damage.
Cleaning and Maintenance Protocols
Cleaning technical woven fabrics requires careful consideration of the material’s composition and the type of contamination. Gentle cleaning methods are often recommended to prevent damage to the fabric’s structure or finish.
- Inspect the fabric for any specific cleaning instructions.
- Use soft-bristled brushes or clean, dry cloths for removing surface debris.
- Avoid harsh chemicals unless specified by the manufacturer.
Extending Service Life
Regular inspection and maintenance are key to extending the service life of technical woven fabrics. This includes monitoring for signs of wear, addressing any damage promptly, and ensuring that the fabric is used within its designed specifications.
Conclusion
Technical woven fabrics, including carbon fiber, glass fiber, aramid, and Kevlar, have revolutionized various industries with their exceptional properties and diverse applications. This guide has explored the composition, characteristics, and uses of these high-performance materials, providing a thorough understanding of their benefits and limitations.
When selecting a technical textile, it’s crucial to consider factors such as strength, weight, durability, and cost. By understanding the unique properties of each material, industries can make informed decisions to optimize their products and processes. Whether it’s for aerospace, automotive, or safety applications, the right woven fabric can significantly enhance performance and efficiency.
The future of technical textiles looks promising, with ongoing advancements in manufacturing and treatment options. As research continues to push the boundaries of these materials, we can expect to see even more innovative applications and uses across various sectors. By staying informed about the latest developments in technical woven fabrics, industries can stay ahead of the curve and capitalize on the benefits of these high-performance materials.
FAQ
What are technical woven fabrics?
Technical woven fabrics are engineered materials that offer exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to various environmental factors. They are made from high-performance fibers such as carbon fiber, glass fiber, aramid, and Kevlar.
What is the difference between E-Glass and S-Glass?
E-Glass and S-Glass are types of glass fiber materials. E-Glass is a more common and cost-effective option, while S-Glass has higher strength and stiffness, making it suitable for more demanding applications.
What makes Kevlar different from other aramid fibers?
Kevlar is a specific type of aramid fiber known for its exceptional impact and puncture resistance. Its unique molecular structure and manufacturing process set it apart from other aramid fibers.
How do different weave patterns affect the performance of technical woven fabrics?
The weave pattern of a technical woven fabric can significantly impact its performance. Different weave patterns, such as plain weave, twill weave, and satin weave, offer varying levels of strength, flexibility, and resistance to different environmental factors.
What are the benefits of using hybrid fabric solutions?
Hybrid fabric solutions combine the benefits of different materials, offering a balance of properties such as strength, weight, and cost. This can be particularly useful in applications where a single material may not meet all the required specifications.
How should technical woven fabrics be stored and handled?
Technical woven fabrics should be stored in a dry, cool environment, away from direct sunlight and moisture. They should be handled carefully to avoid damage, and cleaning and maintenance protocols should be followed as recommended by the manufacturer.
What are the key considerations when sourcing technical woven fabrics?
When sourcing technical woven fabrics, it’s essential to evaluate manufacturer specifications, understand testing and certification standards, and consider factors such as quality, reliability, and cost.
Can technical woven fabrics be used in high-temperature applications?
Some technical woven fabrics, such as aramid and Kevlar, are known for their heat and flame resistance, making them suitable for high-temperature applications. However, the specific temperature range and performance will depend on the material and its treatment.
How do I choose the right technical woven fabric for my application?
Choosing the right technical woven fabric involves considering factors such as strength, weight, durability, and cost, as well as the specific requirements of your application. It’s essential to compare the properties and benefits of different materials and weave patterns to make an informed decision.