5 Tips to Distinguish Fiberglass and Carbon Fiber Products
Before you read this article, watch an interesting short video first:
When it comes to choosing the right material for your project, understanding the differences between fiberglass and carbon fiber is crucial. With both materials possessing distinct properties and characteristics, making an informed decision can be daunting. In this article, we'll provide you with five essential tips that will help you distinguish between fiberglass and carbon fiber products.
Key Takeaways
- Fiberglass and carbon fiber are two different composites with unique properties.
- Appearance, weight, strength, cost, application, manufacturing processes, and maintenance are crucial factors to consider when choosing between fiberglass and carbon fiber.
- Fiberglass is commonly used in industries like construction, automotive, and marine due to its strength, durability, and versatility.
- Carbon fiber is known for its lightweight, high-strength, and stiffness, making it popular in industries such as aerospace, sports equipment, and luxury cars.
- While fiberglass is generally more affordable than carbon fiber, the price can vary depending on the application and manufacturing process.
What is Fiberglass?

Fiberglass is a composite material consisting of fine fibers of glass. These fibers are woven together to create a strong and durable material with a range of applications in various industries.
Fiberglass is known for its versatility and is commonly used in the construction of boats, sports equipment, and home insulation, among other things.
Manufacturing fiberglass involves a process known as filament winding, where continuous glass filaments are impregnated with resin and wound onto a mold. The resulting material is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to work with.
"Fiberglass allows for strong and durable products which are also lightweight and easy to handle"
What is Carbon Fiber?
Carbon fiber is a lightweight and exceptionally strong material composed of thin fibers primarily made from carbon atoms. These fibers are woven together to provide increased durability and resistance to bending and twisting, making it extremely popular in a variety of industries. Aside from being known for its remarkable strength and stiffness, it also has a very low thermal expansion coefficient, making it an ideal material for applications in extreme temperature environments like aerospace and motorsports.
One of the unique characteristics of carbon fiber is its anisotropic nature. This means that its properties differ depending on the direction of the fibers. Carbon fiber is significantly lighter than other common materials like steel and aluminum that have similar strength. This makes it a popular choice for aerospace components, high-performance cars, and sport equipment.
In the table below, we'll take a closer look at some of the properties and characteristics of carbon fiber that make it a popular choice in various industries.
| Properties | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Strength | High tensile strength, stiffness, and resistance to bending and twisting. |
| Weight | Significantly lighter than other common materials like steel and aluminum. |
| Heat resistance | Low thermal expansion coefficient, making it ideal for use in extreme temperature environments. |
| Appearance | Glossy and high-tech look with a distinct woven pattern. |
Overall, carbon fiber is a highly sought-after material in multiple industries. With its unique combination of strength, stiffness, and lightness, it provides unparalleled performance and versatility for a massive range of applications.
Appearance Differences
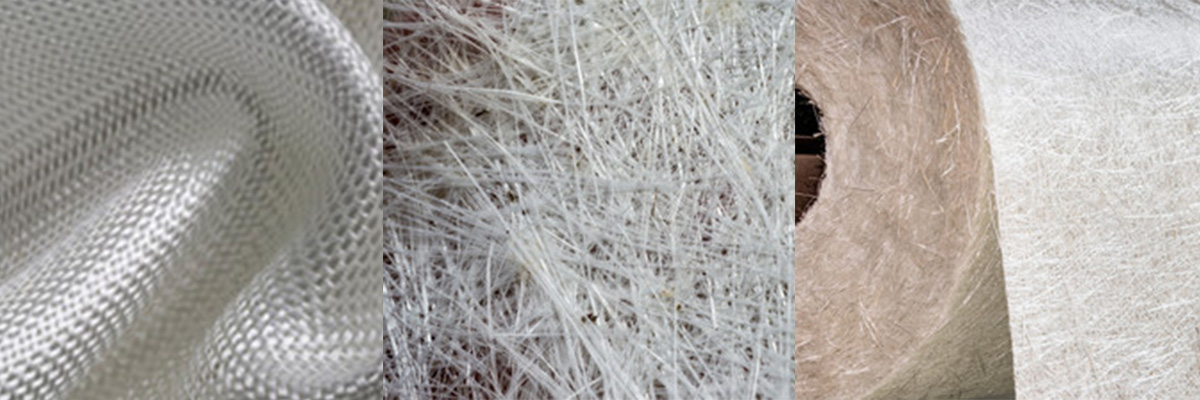
If you're trying to differentiate between fiberglass and carbon fiber products, one of the most noticeable differences is their appearance. Fiberglass typically has a more matte or semi-glossy finish, while carbon fiber has a distinct woven pattern that gives it a glossy, high-tech look that many enthusiasts find visually appealing.
When you look closely at a fiberglass product, you may notice small bumps or ridges on the surface, which are a result of the manufacturing process. Carbon fiber products, on the other hand, generally have a smoother surface due to the intricate weaving process that occurs during their make.Fun fact:
If you run your hand across a carbon fiber product, you may feel a slight texture due to the criss-crossing pattern of the fibers.
Weight Differences
When it comes to weight, carbon fiber takes the lead. It is significantly lighter than fiberglass thanks to its composition of thin carbon fibers. This makes it ideal for applications that require strength and durability without the added weight.
Although fiberglass is not as lightweight as carbon fiber, it is still a relatively light material when compared to other alternatives. It remains a popular choice in industries such as construction and marine where weight is not as crucial of a factor.
Strength and Stiffness Differences
One significant difference between fiberglass and carbon fiber products is their strength and stiffness. Carbon fiber has a higher strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness compared to fiberglass. When tested under similar conditions, carbon fiber products have shown to be stronger and stiffer than their fiberglass counterparts.
For example, according to a study, a carbon fiber-reinforced plastic (CFRP) strut showed a 35% increase in stiffness and a 12% increase in strength than a similar fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) strut. These findings emphasize the superior performance of carbon fiber and its ability to handle more significant loads without succumbing to bending or twisting.
While fiberglass is still used in many applications and offers a good balance of strength and affordability, carbon fiber presents a superior option with exceptional strength and stiffness properties. As technology continues to advance, carbon fiber's full potential is yet to be explored for future applications and industries.
Cost Differences
When choosing between fiberglass and carbon fiber products, cost is often a key factor to consider. Fiberglass is generally more affordable than carbon fiber due to its easier manufacturing process and a lower cost of materials.
However, it's important to note that the price of both materials can vary greatly depending on the intended application and manufacturing process used.
| Material | Cost (per pound) |
|---|---|
| Fiberglass | $1 to $5 |
| Carbon Fiber | $10 to $30 |
These costs are estimates and can vary depending on the supplier and other factors.
It's also worth noting that while carbon fiber may initially seem more expensive than fiberglass, its lightweight nature can result in significant cost savings in applications where reducing weight can lead to greater efficiency and performance.
Application Differences
When it comes to applications, fiberglass and carbon fiber have distinct uses due to their unique properties.
Fiberglass is commonly used in:
- Boat hulls and decks
- Swimming pools and spas
- Home insulation and roofing
- Automotive body parts
On the other hand, carbon fiber finds its way in various high-performance applications, such as:
- Aerospace structures and components
- Sports equipment such as bicycles, golf clubs, and ski poles
- Luxury car components such as hoods and spoilers
- Medical prosthetics
While fiberglass is more affordable and is widespread use, carbon fiber shines in more advanced and specialized applications that require exceptional strength and stiffness in a lightweight material.
Manufacturing Processes
Both fiberglass and carbon fiber have unique manufacturing processes that impact their properties and applications. Fiberglass is typically manufactured using the filament winding process, in which continuous glass filaments are impregnated with resin and wound in a specific pattern onto a cylindrical mold.
On the other hand, carbon fiber often involves the use of a carbon fiber fabric, sheet, or tow, which is impregnated with resin and cured under heat and pressure. The specific manufacturing process used can vary depending on the intended application, the desired strength and weight of the final product, and other factors.
Did you know? Carbon fiber composites were first developed in the 1960s for aerospace applications.
Fiberglass manufacturing processes are often simpler and more cost-effective than those used for carbon fiber. However, the strength and stiffness of carbon fiber composites make them ideal for high-performance applications in industries such as aerospace, sports equipment, and automotive.
Maintenance and Durability Differences
Both fiberglass and carbon fiber are known for their durable and long-lasting properties. However, maintenance practices and handling can affect their longevity. Carbon fiber products exhibit better resistance to UV radiation, corrosion, and fatigue than fiberglass.
Regular maintenance and proper handling are essential for extending the lifespan of both materials. Avoid exposing fiberglass and carbon fiber products to extreme temperatures and direct sunlight. Clean them regularly using mild soap and water to prevent dirt accumulation that can cause scratches and abrasions.
"Proper maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of your fiberglass and carbon fiber products while ensuring they stay in excellent condition. Neglecting these maintenance practices can significantly reduce their performance and durability."
If you notice any cracks or damages, repair them immediately to prevent further degradation of the products. Seek professional assistance if necessary to ensure proper repair and maintenance.
Conclusion
There you have it! Five essential tips to help you distinguish between fiberglass and carbon fiber products. By understanding the differences between these two materials, you can make informed decisions when it comes to purchasing or working with them. Consider factors like appearance, weight, strength, cost, application, manufacturing processes, and maintenance to determine which material is the right fit for your specific needs.
Whether you're looking for high-performance sports equipment or durable boat hulls, understanding the differences between fiberglass and carbon fiber can make all the difference. So, be sure to keep these tips in mind and choose wisely. Happy shopping!
FAQ
What is fiberglass?
Fiberglass is a composite material made up of fine fibers of glass. It is commonly used in various industries, including automotive, construction, and marine, due to its strength, durability, and versatility.
What is carbon fiber?
Carbon fiber is a lightweight and high-strength material composed of thin fibers primarily made from carbon atoms. It is known for its exceptional performance in industries like aerospace, sports equipment, and automotive.
How can I distinguish between fiberglass and carbon fiber products based on their appearance?
Fiberglass typically has a more matte or semi-glossy finish, whereas carbon fiber has a distinct woven pattern that gives it a glossy, high-tech look.
What is the difference in weight between fiberglass and carbon fiber?
Carbon fiber is significantly lighter than fiberglass, making it desirable for applications that require reduced weight while maintaining strength.
How do fiberglass and carbon fiber differ in terms of strength and stiffness?
Carbon fiber exhibits a higher strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness compared to fiberglass, making carbon fiber products more resistant to bending and twisting, providing superior performance and durability.
Which is more affordable, fiberglass or carbon fiber?
Generally, fiberglass is more affordable than carbon fiber, although the price can vary depending on the specific application and manufacturing process.
In which applications is fiberglass commonly used?
Fiberglass is widely used in applications such as boat hulls, swimming pools, and home insulation.
Where is carbon fiber often found?
Carbon fiber is often found in high-performance sports equipment, aircraft parts, and luxury car components.
How are fiberglass and carbon fiber manufactured?
Fiberglass is commonly manufactured using a process called filament winding, where continuous glass filaments are impregnated with resin and wound onto a mold. Carbon fiber involves the curing and heating of carbon fiber sheets or fabrics.
How do fiberglass and carbon fiber differ in terms of maintenance and durability?
While both fiberglass and carbon fiber are known for their durability, carbon fiber exhibits better resistance to corrosion, UV radiation, and fatigue over time. Regular maintenance and proper handling are essential for extending the lifespan of both materials.