Carbon Fiber Filament VS Carbon Fiber Yarn
-
 Your Composites Expert Carbon Fiber Materials&Products
Your Composites Expert Carbon Fiber Materials&Products -
-1.png?width=686&height=617) Your Composites Expert Aramid Fiber Materials&Products
Your Composites Expert Aramid Fiber Materials&Products -
 Your Composites Expert UHMWPE Materials&Products
Your Composites Expert UHMWPE Materials&Products -
 Your Composites Expert Fiberglass Materials&Products
Your Composites Expert Fiberglass Materials&Products -
 Your Composites ExpertPBO Materials&Products
Your Composites ExpertPBO Materials&Products -
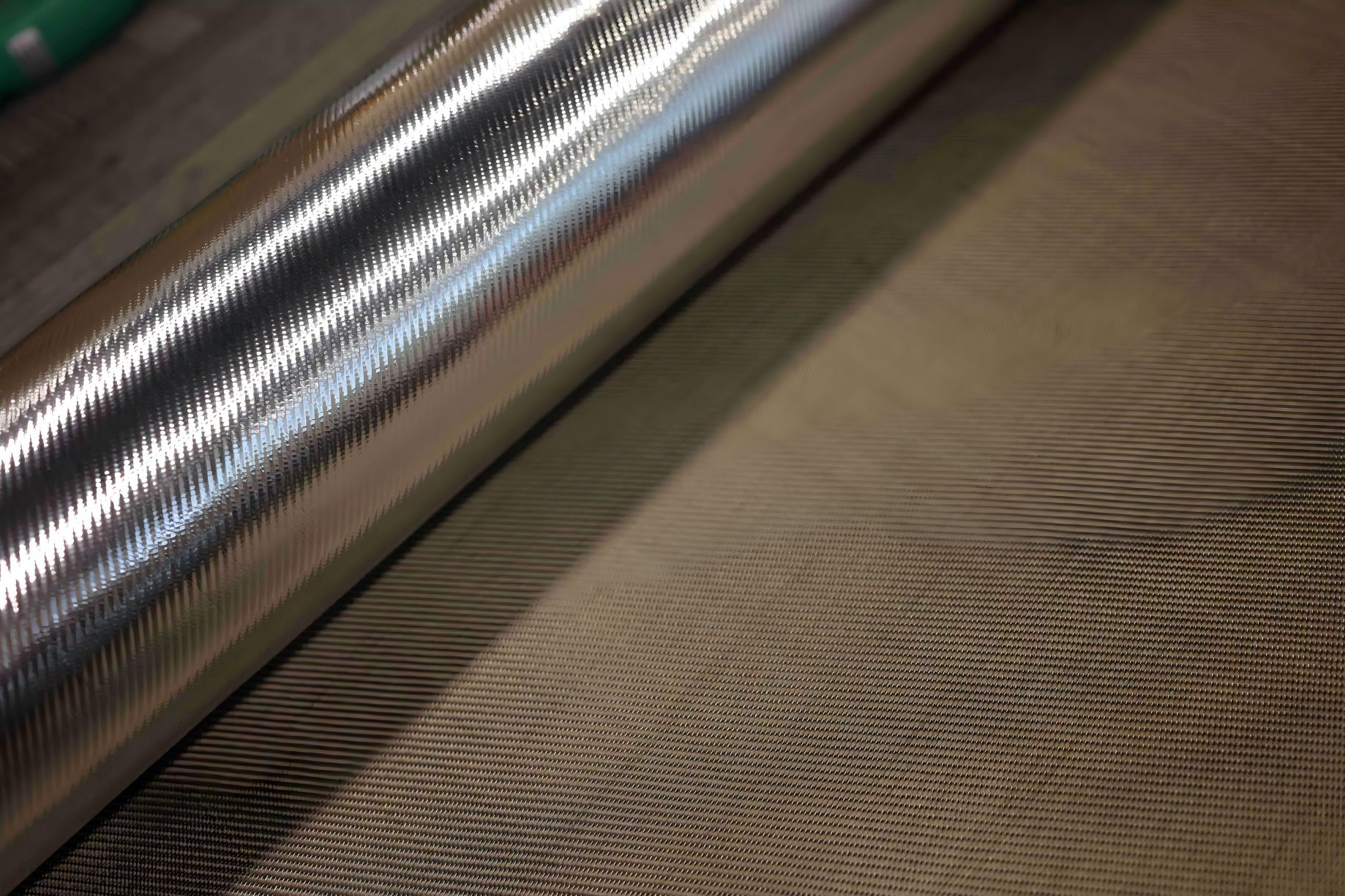 Your Composites Expert Basalt Materials&Products
Your Composites Expert Basalt Materials&Products
Carbon fiber is a popular reinforcement material used in various applications, including aerospace, automotive, civil engineering, and sports. The lightweight, high strength, and stiffness properties of carbon fiber make it an ideal material for structures that require high performance and durability.
Carbon fiber raw material comes in two primary forms: filament and yarn. Although they both comprise carbon fibers, there are significant differences between the two materials in terms of structure, properties, and applications.
Carbon Fiber Filament

Carbon fiber filament refers to strands of thin, continuous fibers that are twisted or woven together to form a stronger, more durable material. The fibers are typically less than 10 microns in diameter and can be aligned in any direction, depending on the application. Carbon fiber filaments are manufactured by a process called pyrolysis, in which carbon fiber precursors are heated to high temperatures in an oxygen-free environment to eliminate all non-carbon atoms.
Carbon fiber filaments have excellent strength-to-weight and stiffness-to-weight ratios, making them an ideal reinforcement material for composites. It can be combined with various matrices, such as epoxy, to form carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites. CFRPs are used in high-performance applications, including racing cars, aircraft, and sporting equipment.
Carbon fiber filaments are relatively expensive and require specialized equipment for processing. The manufacturing process involves high-temperature and high-pressure conditions, making it energy-intensive and costly. However, it also offer superior strength and durability compared to other materials, such as steel and aluminum, making it a preferred material for high-performance applications.
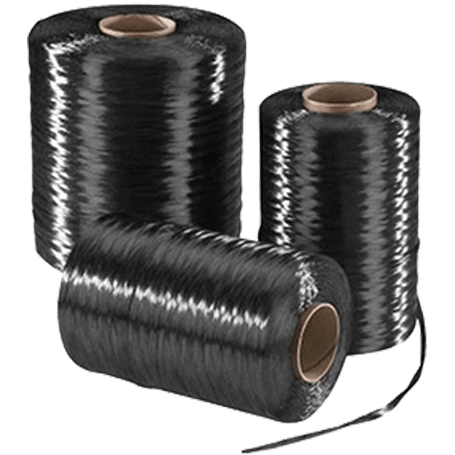
Carbon Fiber Yarn
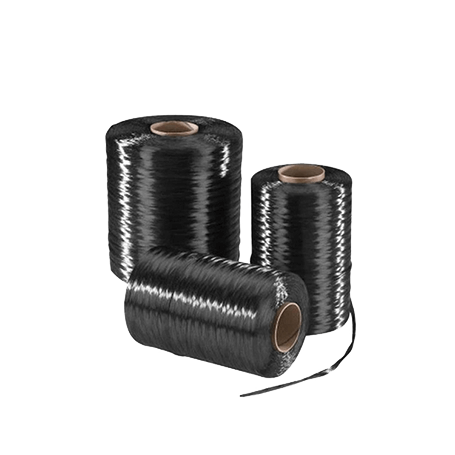

Carbon fiber yarn, on the other hand, is composed of multiple strands of continuous carbon fibers twisted or braided together to form a thicker, more robust material. The strands range from a few microns to several millimeters in diameter, depending on the application. They are manufactured using either a wet or dry spinning process, in which carbon fiber precursors are spun into a fibrous material and then heat-treated to carbonize them.
Compared to carbon fiber filaments, carbon fiber yarns are less expensive and easier to process. Due to their thicker diameter, carbon fiber yarns are often used in applications where mechanical properties are not as critical, such as textiles, ropes, and cordage.
One of the primary advantages of carbon fiber yarn is its versatility. Carbon fiber yarn can be woven or knitted into various forms, including fabrics, tapes, and braids, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Carbon fiber fabrics, for example, are commonly used in high-end sports equipment, such as golf clubs and tennis rackets, as well as in automotive and aerospace applications.
Comparison between Carbon Fiber Filament and Carbon Fiber Yarn
Although carbon fiber filament and yarn both offer excellent strength and stiffness properties, there are several significant differences between the two materials. These differences include:
- Manufacturing process
Carbon fiber filaments are manufactured using a pyrolysis process that involves heating carbon fiber precursors at high temperatures in an oxygen-free environment. The process is energy-intensive and expensive, requiring specialized equipment. Carbon fiber yarn, on the other hand, is manufactured using either a wet or dry spinning process that is less energy-intensive and less costly.
- Structure
Carbon fiber filaments are thin, continuous fibers that are twisted or woven together to form a stronger, more durable material. Carbon fiber yarn, on the other hand, is composed of multiple strands of carbon fibers twisted or braided together to form a thicker, more robust material.
- Diameter
Carbon fiber filaments are typically less than 10 microns in diameter, while carbon fiber yarns range from a few microns to several millimeters in diameter.
- Applications
Carbon fiber filaments are commonly used in high-performance applications, such as racing cars, aircraft, and sporting equipment, where strength and durability are critical. Carbon fiber yarns, on the other hand, are used in a wide range of applications, including textiles, ropes, and cordage, where mechanical properties are not as critical.
Conclusion
In conclusion, carbon fiber filament and carbon fiber yarn are two forms of carbon fiber that offer excellent strength and stiffness properties. Although they both comprise carbon fibers, they differ in terms of manufacturing process, structure, diameter, and applications. Carbon fiber filament is a more expensive and durable material used in high-performance applications, whereas carbon fiber yarn is a versatile and less costly material used in various applications. Overall, carbon fiber is a preferred material in many industries due to its lightweight, high strength, and stiffness properties, making it a widely adopted technology in the future.