EE. UU. impulsa importaciones de fibra de carbono en medio de escasez interna
-
Tabla de contenido
“U.S. Accelerates Carbon Fiber Imports to Bridge Domestic Supply Gap.”
The United States is experiencing a significant increase in carbon fiber imports due to a growing domestic shortage of this critical material. As industries such as aerospace, automotive, and renewable energy expand their reliance on lightweight and high-strength materials, the demand for carbon fiber has surged. This situation has prompted U.S. manufacturers to seek alternative sources from international markets to meet production needs and maintain competitiveness. The shift highlights the challenges faced by domestic producers and the strategic importance of securing a stable supply of carbon fiber for future technological advancements and sustainability efforts.
U.S. Carbon Fiber Import Trends and Market Impact
In recent years, the U.S. has witnessed a significant shift in its carbon fiber import trends, primarily driven by a domestic shortage that has prompted manufacturers to seek alternative sources. Carbon fiber, known for its lightweight and high-strength properties, is a critical material in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and renewable energy. As demand for carbon fiber continues to rise, the U.S. market has increasingly turned to international suppliers to bridge the gap created by insufficient domestic production capabilities.
The surge in carbon fiber imports can be attributed to several factors. First and foremost, the rapid expansion of industries that utilize carbon fiber has outpaced the growth of domestic production. For instance, the aerospace sector, which relies heavily on carbon fiber for aircraft components, has experienced a boom in demand due to increased air travel and the development of new aircraft models. Similarly, the automotive industry is transitioning towards lighter materials to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, further driving the need for carbon fiber. Consequently, U.S. manufacturers have found themselves in a precarious position, unable to meet the escalating demand with local resources alone.
In response to this challenge, U.S. companies have turned to international markets, particularly those in Asia and Europe, where carbon fiber production is more established and often more cost-effective. Countries such as Japan and China have emerged as key players in the global carbon fiber market, offering competitive pricing and advanced manufacturing techniques. As a result, U.S. imports of carbon fiber have surged, reflecting a strategic shift in sourcing practices aimed at ensuring a steady supply of this essential material.
Moreover, the increasing reliance on imported carbon fiber has significant implications for the U.S. market. On one hand, it allows manufacturers to maintain production levels and meet customer demands without interruption. However, this dependence on foreign suppliers also raises concerns about supply chain vulnerabilities. Geopolitical tensions, trade policies, and fluctuations in international markets can all impact the availability and cost of imported carbon fiber, potentially leading to disruptions in production and increased prices for end-users.
Furthermore, the growing importation of carbon fiber has sparked discussions about the future of domestic manufacturing. While the immediate solution to the shortage may lie in imports, there is a pressing need for investment in domestic production capabilities. Industry stakeholders are advocating for policies that support the development of local manufacturing facilities and research initiatives aimed at enhancing carbon fiber production technologies. By fostering a robust domestic supply chain, the U.S. can mitigate risks associated with reliance on foreign imports and position itself as a leader in the carbon fiber market.
In conclusion, the U.S. carbon fiber import trends reflect a complex interplay between rising demand and domestic production limitations. As manufacturers increasingly turn to international sources to fulfill their needs, the implications for the market are profound. While imports provide a temporary solution to the shortage, they also highlight the necessity for strategic investments in domestic capabilities. Moving forward, a balanced approach that combines the benefits of global sourcing with the development of local production will be essential for ensuring the long-term sustainability and competitiveness of the U.S. carbon fiber industry.
The Role of Carbon Fiber in U.S. Manufacturing
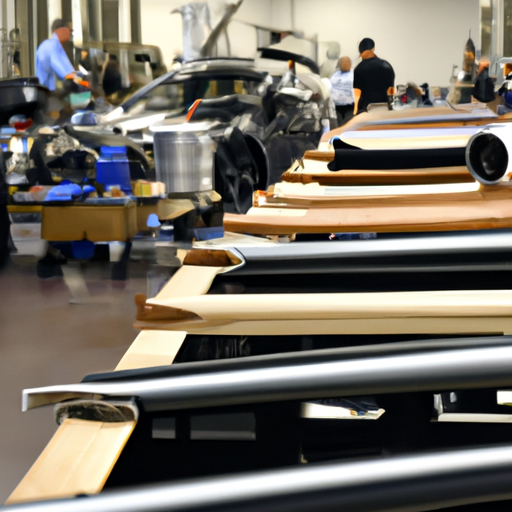

Carbon fiber has emerged as a critical material in the landscape of U.S. manufacturing, playing a pivotal role in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods. Its unique properties, such as high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and rigidity, make it an ideal choice for applications where performance and efficiency are paramount. As the demand for lightweight and durable materials continues to rise, the significance of carbon fiber in enhancing product performance cannot be overstated. Consequently, the U.S. manufacturing sector is increasingly reliant on this advanced composite material to meet both consumer expectations and regulatory standards.
In the aerospace industry, for instance, carbon fiber is integral to the production of aircraft components. The use of carbon fiber in wings, fuselages, and other structural elements allows manufacturers to reduce weight, which in turn improves fuel efficiency and overall performance. As airlines seek to lower operational costs and minimize their environmental impact, the demand for carbon fiber-reinforced components has surged. This trend is further amplified by the growing emphasis on sustainability within the industry, as lighter aircraft contribute to lower carbon emissions. However, the domestic supply of carbon fiber has struggled to keep pace with this burgeoning demand, prompting manufacturers to look beyond U.S. borders for reliable sources.
Similarly, the automotive sector has recognized the advantages of carbon fiber in the quest for more efficient vehicles. With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and the increasing focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions, automakers are turning to carbon fiber to enhance vehicle performance while maintaining safety standards. The lightweight nature of carbon fiber allows for greater battery efficiency and extended range, making it a valuable asset in the design of next-generation vehicles. As a result, the automotive industry is experiencing a shift towards incorporating more carbon fiber components, further driving the need for increased imports to supplement domestic production.
Moreover, the sporting goods industry has also embraced carbon fiber, utilizing it in high-performance equipment such as bicycles, tennis rackets, and fishing rods. The material’s ability to provide strength without adding excessive weight has made it a favorite among athletes and enthusiasts alike. As consumer preferences shift towards high-quality, performance-oriented products, manufacturers are compelled to invest in carbon fiber technologies to remain competitive. This growing reliance on carbon fiber across various sectors underscores the material’s importance in modern manufacturing.
Despite its advantages, the U.S. faces challenges in scaling up domestic carbon fiber production. Factors such as high manufacturing costs, limited production capacity, and the need for specialized expertise have hindered the growth of a robust domestic supply chain. Consequently, the U.S. has increasingly turned to international markets to fulfill its carbon fiber needs. This reliance on imports not only addresses immediate supply shortages but also highlights the necessity for strategic investments in domestic manufacturing capabilities.
In conclusion, carbon fiber plays an indispensable role in U.S. manufacturing, driving innovation and efficiency across multiple industries. As the demand for this advanced material continues to grow, the challenges associated with domestic production must be addressed to ensure a sustainable and competitive manufacturing landscape. By bolstering domestic capabilities while strategically leveraging international resources, the U.S. can position itself to meet the evolving needs of its manufacturing sector and maintain its leadership in the global market.
Challenges and Opportunities in Domestic Carbon Fiber Production
The recent surge in carbon fiber imports into the United States highlights a significant challenge facing the domestic production landscape. As industries increasingly turn to carbon fiber for its lightweight and high-strength properties, the domestic supply has struggled to keep pace with growing demand. This situation presents both challenges and opportunities for U.S. manufacturers, policymakers, and investors alike.
One of the primary challenges in domestic carbon fiber production is the high cost associated with manufacturing processes. The production of carbon fiber is capital-intensive, requiring advanced technology and significant investment in research and development. As a result, many U.S. manufacturers find it difficult to compete with international suppliers, particularly those in countries where labor and production costs are lower. This disparity has led to a reliance on imports, which, while providing immediate relief to industries in need, raises concerns about long-term sustainability and national security.
Moreover, the domestic carbon fiber industry faces additional hurdles, such as limited access to raw materials and a fragmented supply chain. The production of carbon fiber begins with precursor materials, primarily polyacrylonitrile (PAN), which are often sourced from a limited number of suppliers. This reliance on a narrow supply base can create vulnerabilities, particularly in times of geopolitical tension or trade disputes. Consequently, the U.S. must consider strategies to bolster its domestic supply chain, ensuring that manufacturers have reliable access to the materials necessary for production.
Despite these challenges, the current landscape also presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation within the domestic carbon fiber sector. As industries such as aerospace, automotive, and renewable energy increasingly adopt carbon fiber for its performance advantages, there is a pressing need for U.S. manufacturers to scale up production capabilities. This demand can drive investment in new technologies and processes that enhance efficiency and reduce costs, ultimately making domestic production more competitive.
Furthermore, government initiatives aimed at fostering advanced manufacturing can play a crucial role in revitalizing the carbon fiber industry. By providing financial incentives, grants, and support for research and development, policymakers can encourage companies to invest in domestic production facilities. Such initiatives not only help to create jobs but also contribute to the overall resilience of the U.S. manufacturing sector, reducing dependence on foreign imports.
In addition to government support, collaboration between industry stakeholders can also pave the way for innovation. Partnerships between manufacturers, research institutions, and universities can facilitate the sharing of knowledge and resources, leading to breakthroughs in production techniques and material science. By fostering a collaborative ecosystem, the U.S. can position itself as a leader in carbon fiber technology, enhancing its competitive edge in the global market.
In conclusion, while the challenges facing domestic carbon fiber production are significant, they are not insurmountable. The current reliance on imports underscores the urgent need for strategic investments and collaborative efforts to strengthen the U.S. supply chain. By addressing these challenges head-on, the nation can seize the opportunity to enhance its manufacturing capabilities, drive innovation, and ultimately secure a more sustainable and competitive future in the carbon fiber industry. As the demand for lightweight, high-performance materials continues to grow, the potential for a robust domestic carbon fiber sector remains ripe for exploration and development.
Preguntas y respuestas
1. **Question:** Why is the U.S. increasing carbon fiber imports?
**Answer:** The U.S. is boosting carbon fiber imports to address a domestic shortage that is impacting various industries, including aerospace and automotive, which rely on this material for lightweight and high-strength applications.
2. **Question:** What industries are most affected by the carbon fiber shortage in the U.S.?
**Answer:** The aerospace and automotive industries are the most affected, as they require carbon fiber for manufacturing components that enhance performance and fuel efficiency.
3. **Question:** What are the potential implications of relying on imported carbon fiber?
**Answer:** Relying on imported carbon fiber may lead to supply chain vulnerabilities, increased costs, and potential delays in production for U.S. manufacturers, as well as concerns over quality and consistency of the imported materials.The increase in U.S. carbon fiber imports amid a domestic shortage highlights the growing demand for advanced materials in various industries, particularly aerospace and automotive. This reliance on foreign sources underscores the need for the U.S. to enhance its domestic production capabilities to ensure supply chain stability and meet future market needs. Addressing this shortage could foster innovation, create jobs, and strengthen the overall economy while supporting sustainability efforts.